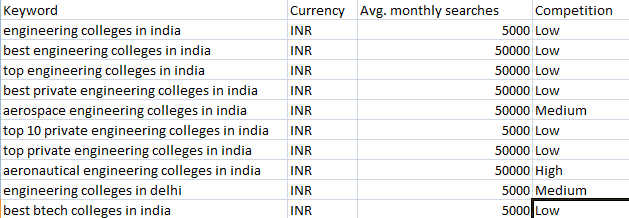
User Experience (UX):–
In the context of digital interfaces such as websites, applications, and software, user experience (UX) refers to the total experience a user has while interacting with a product or service. It includes how the product satisfies the user’s wants and expectations as well as design, usability, and accessibility, among other aspects of the user’s contact with the product.
Usability:
This relates to the product’s ease of use and intuitiveness. Users may accomplish their objectives fast and without irritation when usability is high. Clear navigation, effective workflows, and reducing the amount of steps needed to do activities are some examples of how to achieve this.
Design of Interaction (IxD):
The way consumers engage with the product is the main emphasis of interaction design. Buttons, menus, icons, and other interactive components are covered. The objective is to design simple, straightforward interfaces that enable people to finish activities without difficulty.
Architecture of Information (IA):
The structure and arrangement of the product’s content is known as information architecture. The goal is to ensure that users can traverse the system and locate information with ease. This could entail developing taxonomies, sitemaps, and a coherent content flow.
Visual Style:
The whole user experience is greatly influenced by the product’s visual elements, such as layout, color scheme, typography, and photography. Users can navigate the product more easily and enjoy a more aesthetically pleasant experience with a well-designed interface.
Availability:
People with different capacities can utilize the product thanks to accessibility. Designing for users with visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments falls under this category. Regardless of ability, everyone can use items when they are made accessible.
Research on Users:
Understanding user demands, behaviors, and pain areas through data analytics, usability testing, surveys, and interviews is known as user research. Design choices are influenced by this data, which also aids in the development of user-centered products.